Windows Task Manager is a powerful built-in utility for monitoring your PC’s performance. Here’s how to easily track CPU, memory, disk, and network usage to identify resource hogs.
Monitor CPU Performance
To monitor your CPU usage, open Task Manager by right-clicking the Start button and selecting Task Manager or using the keyboard shortcut Ctrl + Shift + Esc.
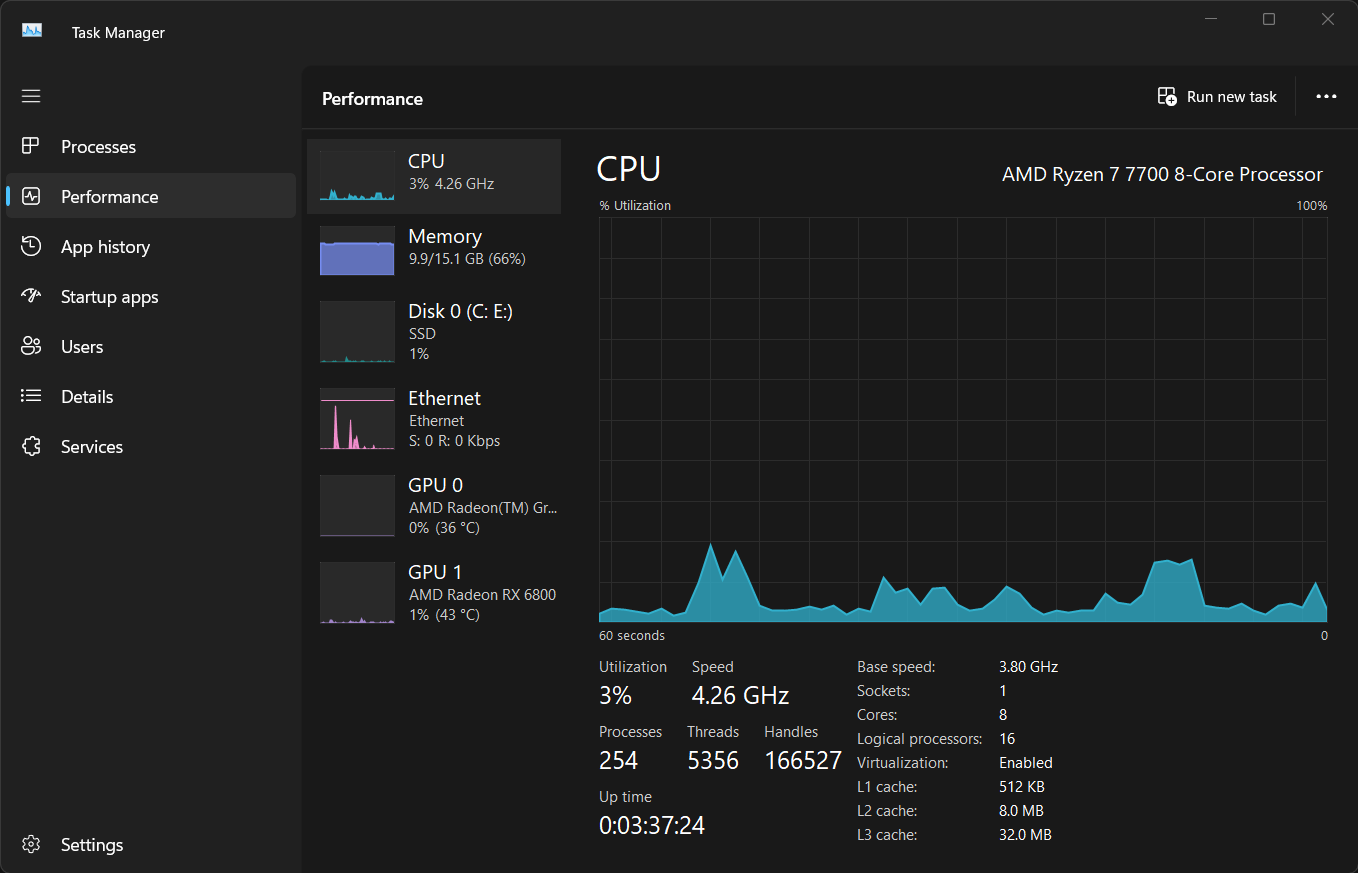
Navigate to the Performance tab and select CPU from the left sidebar to view real-time insights.
The graph displays your CPU usage over time. If the overall usage remains consistently high, head to the Processes tab, sort the list by CPU usage, and look for any resource-hungry applications.
Consider closing these apps. If they’re misbehaving, you can end these tasks by selecting them and clicking End Task near the top.
Below the CPU graph in the Performance tab, you’ll find more detailed information about your CPU. This breaks down the number of cores, base speed, sockets, virtualization support—essentially everything you need to know about your PC.
If the CPU usage here seems suspiciously high, you may need to fix incorrect CPU usage in the Windows Task Manager.
Examine Memory Usage
Sometimes, my PC feels unresponsive. In these cases, it’s often insufficient memory that causes this problem.
If you’re experiencing similar issues, monitoring your RAM usage with Task Manager can help you identify memory hogs. Additionally, you can use the information here to optimize performance and determine if it’s time for an upgrade.
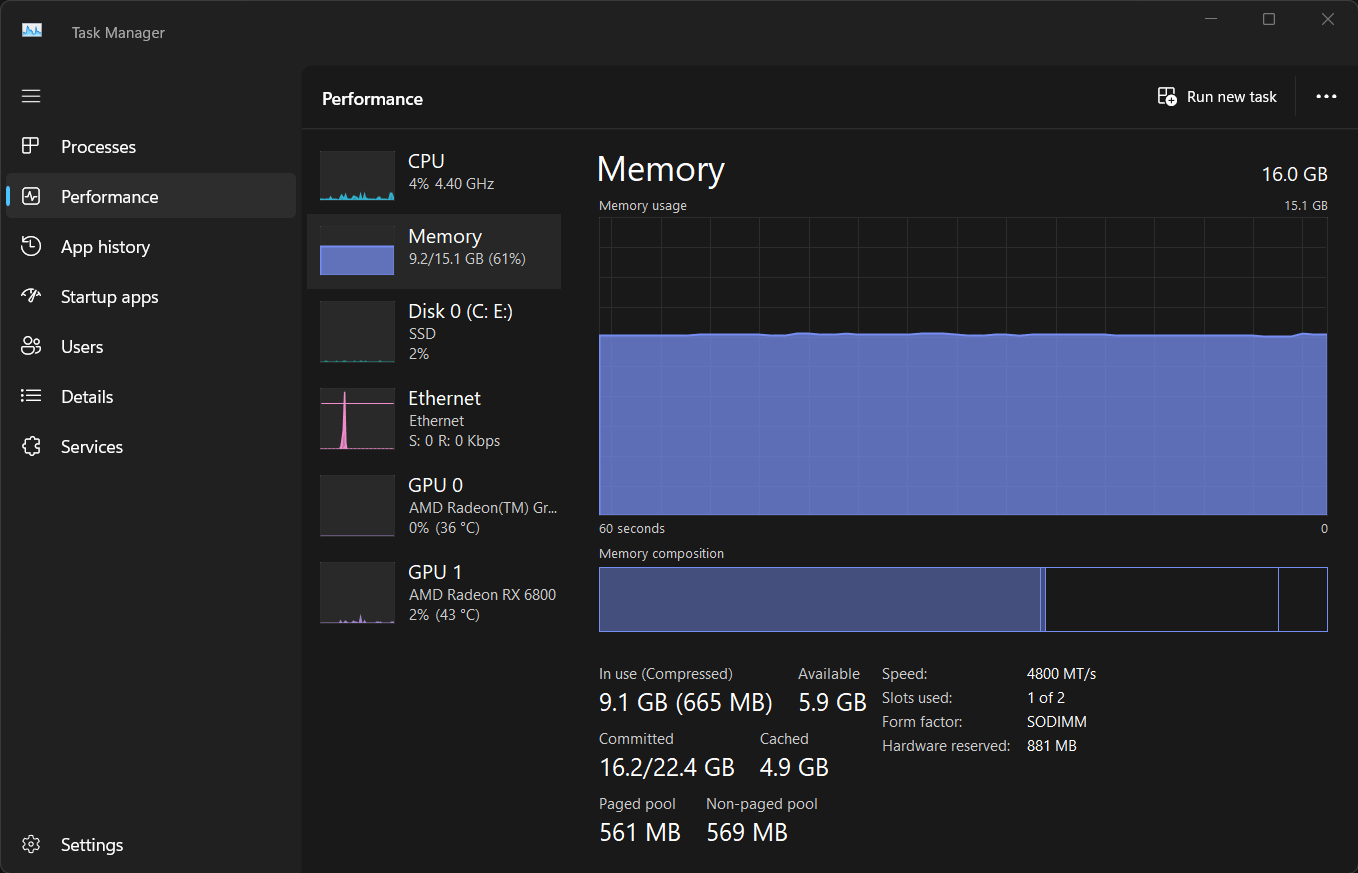
To check your PC’s memory usage, open Task Manager and go to the Performance tab. Select Memory from the left sidebar to view real-time insights into your system’s RAM usage.
The graph shows your current memory usage, with the total amount of RAM and how much is being used. If the In use value is consistently close to the total, your system might be struggling with insufficient memory.
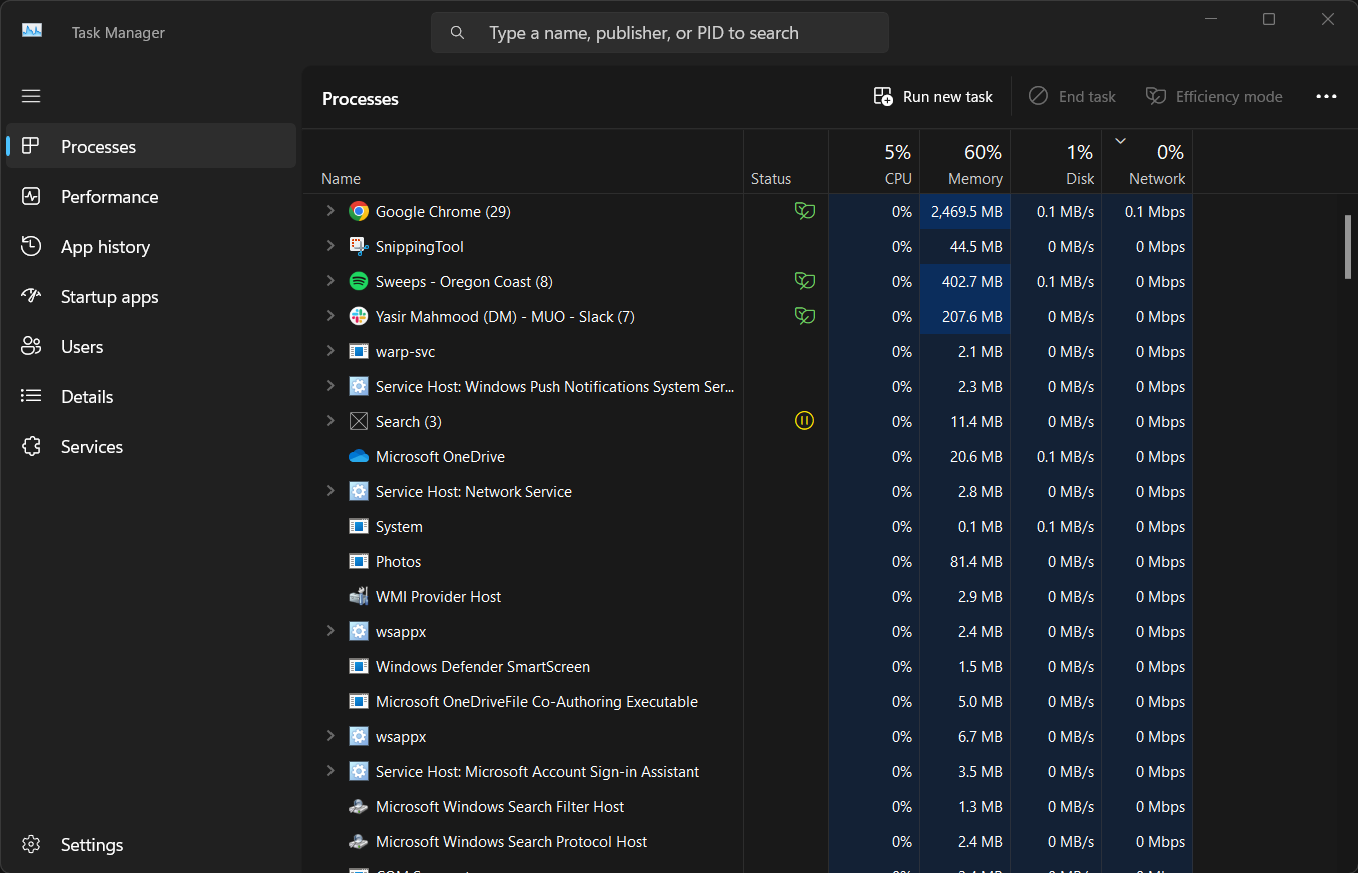
Next, you should switch to the Processes tab and sort by Memory usage to identify memory-hungry apps. Then close unnecessary apps to free up RAM.
If you’re like me and frequently monitor memory, consider changing the Task Manager start page to the Performance tab for quicker access.
However, if you frequently run out of RAM, keep an eye on the Committed value. If this exceeds your total RAM, your system is relying on slow virtual memory, indicating it’s time for an upgrade.
Check Disk Space Usage
Running out of storage space can also cause performance issues on your Windows PC.
To check your disk usage, navigate to the Performance tab in Task Manager. Select your main drive (usually Disk 0) from the left sidebar to view its real-time usage statistics.
The graph shows read and write activity, while the Processes with Disk Activity column displays which apps are currently accessing the disk.
To view per-process disk usage details, switch to the Processes tab. If the Disk column is missing, right-click any column header and select Disk to add it.
You can also enable the search box in the Task Manager to quickly find specific processes. If your main drive is nearly full, consider uninstalling unused apps, moving large files to a good portable SSD, or upgrading to a larger SSD for improved performance and storage capacity.
Analyze Network Usage
Monitoring network usage can help you troubleshoot internet connectivity issues. To view network statistics, navigate to the Performance tab in Task Manager and select Ethernet or Wi-Fi from the left sidebar, depending on your connection type.
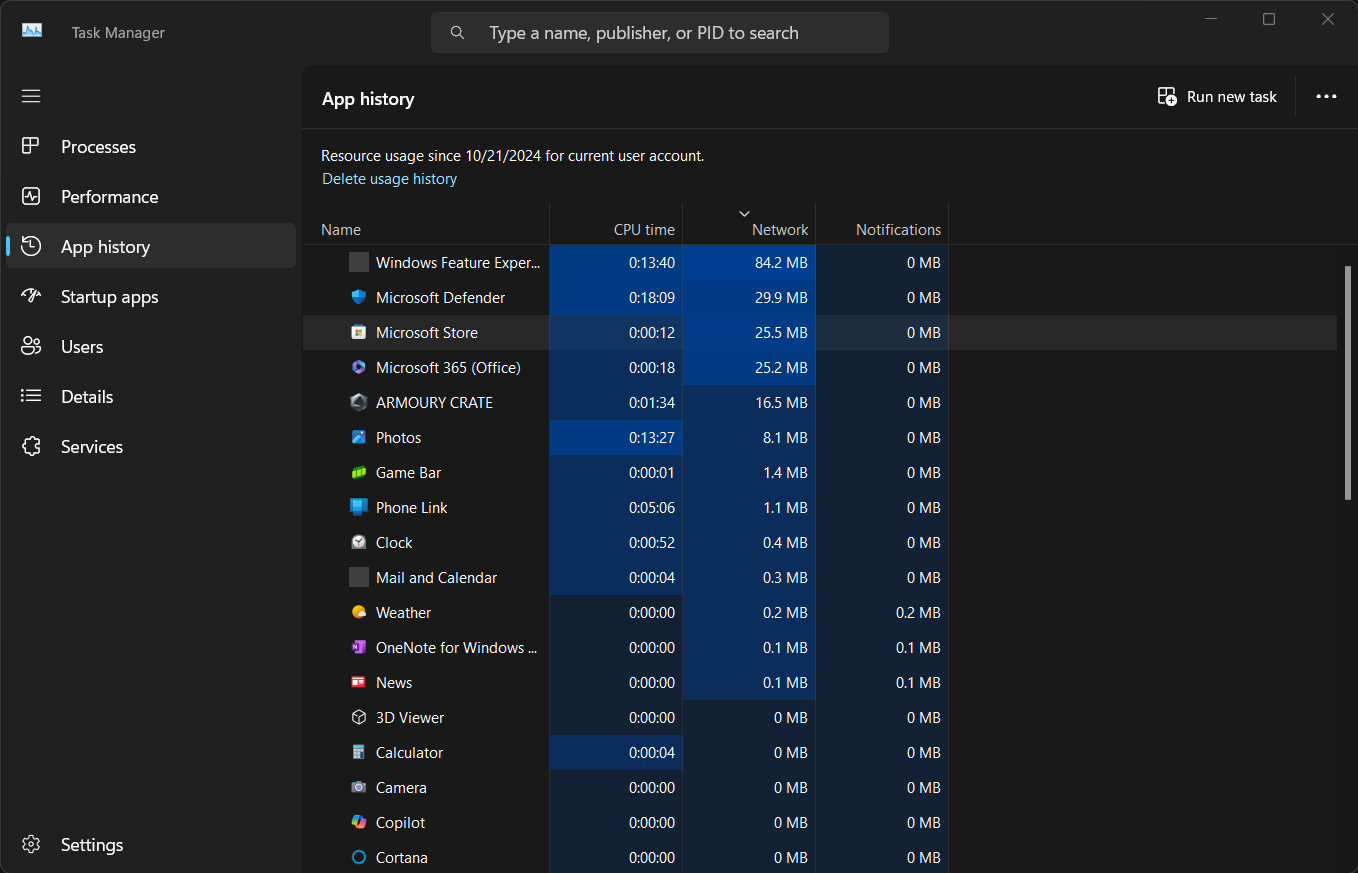
The graph displays real-time network usage, showing the send and receive rates in Mbps. If you notice consistently high usage, switch to the App history tab to identify which applications consume the most network resources.
You can right-click on any column header in the App history tab to add more columns, such as Downloads or Uploads, for more detailed insights into app network usage.
If you suspect a particular app is hogging bandwidth, consider closing it or limiting its network usage through its settings or using third-party tools like NetLimiter.
You can keep your PC running smoothly by monitoring CPU, memory, disk, and network usage with Task Manager. If you notice persistent performance issues during startup, you should optimize your startup apps to reduce resource consumption and keep your PC running as a faster, more responsive system.